Jul 12, 2023The molecular geometry is tetrahedral. Each N atom is sp 3 hybridized and uses one sp 3 hybrid orbital to form the N-N bond, two to form N-H bonds, and one to accommodate a lone pair. The molecular geometry about each N is trigonal pyramidal. … From the number of electron pairs around O in OF 4, predict the hybridization of O. Compare the
Molecular Geometry and Covalent Bonding Models
7.2K This lesson explains orbital hybridization of elements on the periodic table. Understanding of hybridization will allow you to predict how many bonds atoms can make. Related to this
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Here’s a shortcut for how to determine the hybridization of an atom in a molecule that will work in at least 95% of the cases you see in Org 1. For a given atom: Count the number of atoms connected to it (atoms – not bonds!) Count the number of lone pairs attached to it. Add these two numbers together. If it’s 4, your atom is sp3.
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
BF4- lewis structure, molecular geometry, hybridization, bond angle Start by drawing the Lewis structure. The least electronegative atom that is not a hydrogen goes in the center (unless you have been given structural arrangement). Determine the number of electron domains on the central atom. Determine the electron geometry using VSEPR. Correlate the geometry with the hybridization.
Source Image: saylordotorg.github.io
Download Image
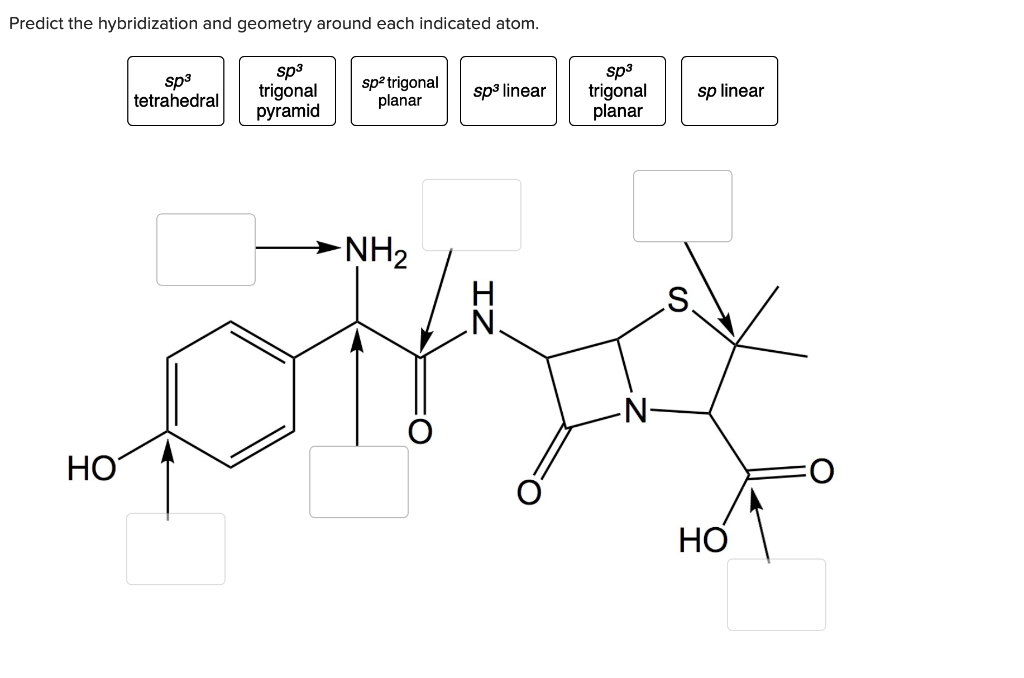
Predict The Hybridization And Geometry Around Each Indicated Atom.
Start by drawing the Lewis structure. The least electronegative atom that is not a hydrogen goes in the center (unless you have been given structural arrangement). Determine the number of electron domains on the central atom. Determine the electron geometry using VSEPR. Correlate the geometry with the hybridization. The central carbon atom has two double bonds to oxygen atoms, and the O-C-O angle is 180 degrees. What is the hybridization around the central carbon atom in CO 2 ? Choose 1 answer:
Molecular Geometry and Covalent Bonding Models
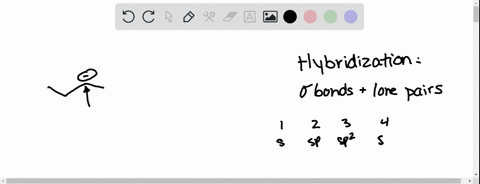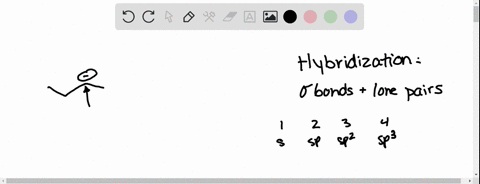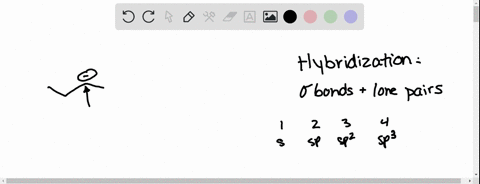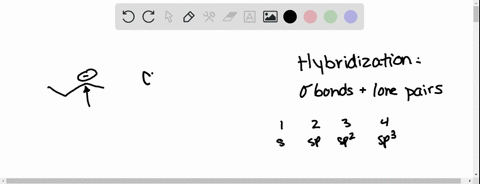
We can find the hybridization of an atom in a molecule by either looking at the types of bonds surrounding the atom or by calculating its steric number. In this video, we use both of these methods to determine the hybridizations of atoms in various organic molecules. Created by Jay. Questions Tips & Thanks Want to join the conversation? Sort by: Molecular Geometry and Covalent Bonding Models

Source Image: saylordotorg.github.io
Download Image
Predict the hybridization, geometry, and bond angles for the cent… | Channels for Pearson+ We can find the hybridization of an atom in a molecule by either looking at the types of bonds surrounding the atom or by calculating its steric number. In this video, we use both of these methods to determine the hybridizations of atoms in various organic molecules. Created by Jay. Questions Tips & Thanks Want to join the conversation? Sort by:

Source Image: pearson.com
Download Image
Molecular Geometry and Covalent Bonding Models Jul 12, 2023The molecular geometry is tetrahedral. Each N atom is sp 3 hybridized and uses one sp 3 hybrid orbital to form the N-N bond, two to form N-H bonds, and one to accommodate a lone pair. The molecular geometry about each N is trigonal pyramidal. … From the number of electron pairs around O in OF 4, predict the hybridization of O. Compare the

Source Image: 2012books.lardbucket.org
Download Image
BF4- lewis structure, molecular geometry, hybridization, bond angle Here’s a shortcut for how to determine the hybridization of an atom in a molecule that will work in at least 95% of the cases you see in Org 1. For a given atom: Count the number of atoms connected to it (atoms – not bonds!) Count the number of lone pairs attached to it. Add these two numbers together. If it’s 4, your atom is sp3.

Source Image: topblogtenz.com
Download Image
Solved Predict the hybridization & geometry around each | Chegg.com Hybridization is a simple model that deals with mixing orbitals to from new, hybridized, orbitals. This is part of the valence bond theory and helps explain bonds formed, the length of bonds, and bond energies; however, this does not explain molecular geometry very well. sp An example of this is acetylene (C 2 H 2 ).
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
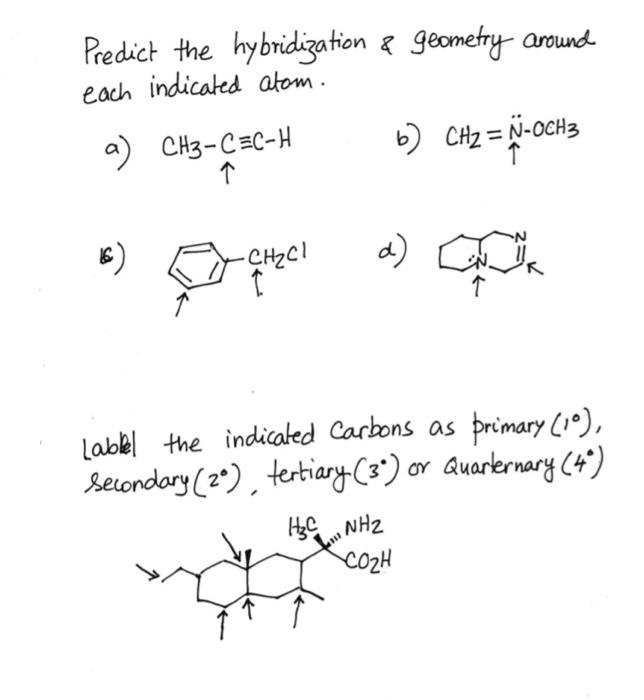
⏩SOLVED:Predict the hybridization and geometry around each… | Numerade Start by drawing the Lewis structure. The least electronegative atom that is not a hydrogen goes in the center (unless you have been given structural arrangement). Determine the number of electron domains on the central atom. Determine the electron geometry using VSEPR. Correlate the geometry with the hybridization.
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Molecular Geometry and Covalent Bonding Models | Molecular geometry, Teaching chemistry, Chemistry lessons The central carbon atom has two double bonds to oxygen atoms, and the O-C-O angle is 180 degrees. What is the hybridization around the central carbon atom in CO 2 ? Choose 1 answer:

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
Predict the hybridization, geometry, and bond angles for the cent… | Channels for Pearson+
Molecular Geometry and Covalent Bonding Models | Molecular geometry, Teaching chemistry, Chemistry lessons 7.2K This lesson explains orbital hybridization of elements on the periodic table. Understanding of hybridization will allow you to predict how many bonds atoms can make. Related to this
BF4- lewis structure, molecular geometry, hybridization, bond angle ⏩SOLVED:Predict the hybridization and geometry around each… | Numerade Hybridization is a simple model that deals with mixing orbitals to from new, hybridized, orbitals. This is part of the valence bond theory and helps explain bonds formed, the length of bonds, and bond energies; however, this does not explain molecular geometry very well. sp An example of this is acetylene (C 2 H 2 ).